

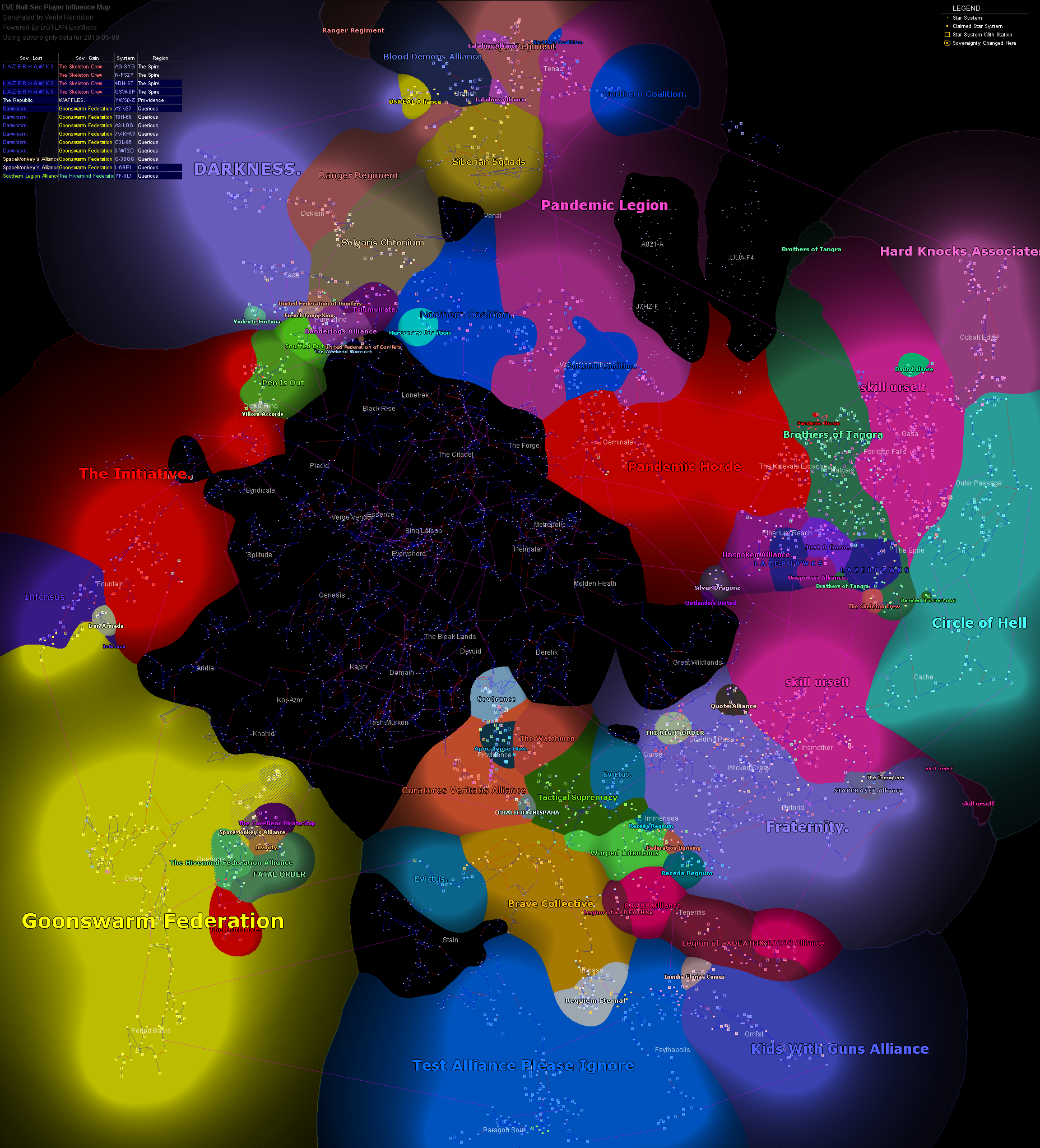
But it does not work with large data tables due to the same reason. With memory tables, there can be a performance boost as the tables are stored in the memory. Memory – Memory tables were formerly known as HEAP.Hence it is ACID-compliant and can efficiently restore your database to the most stable state in case of a crash. InnoDB – InnoDB is the most optimal while choosing an engine to drive performance.This engine makes it easier to migrate the tables into a non-SQL pipeline. CSV engine stores the values in the Comma-separated values (CSV) format.

Mysql querious archive#
ARCHIVE – As the name suggests, Archive helps in archiving the tables by compressing them, in-turn reducing the storage space.MERGE tables use the indexes of the base tables, as they do not have indexes of their own. MERGE – A MERGE table is a virtual table that consolidates different MyISAM tables that have a comparable structure to one table.MyISAM offers big storage, up to 256TB! The tables can also be compressed to get extra storage.
It extends the former ISAM storage engine.
Mysql querious full#
And finally, as said earlier, MySQL is quick and robust.Ĭheck out upGrad’s Full Stack Development Bootcampģ. MySQL has relational databases hence it makes it have methodical storage rather than a big dump of unorganized mess. Even entire developed systems are there that can be referred to for the upcoming projects.
Mysql querious code#
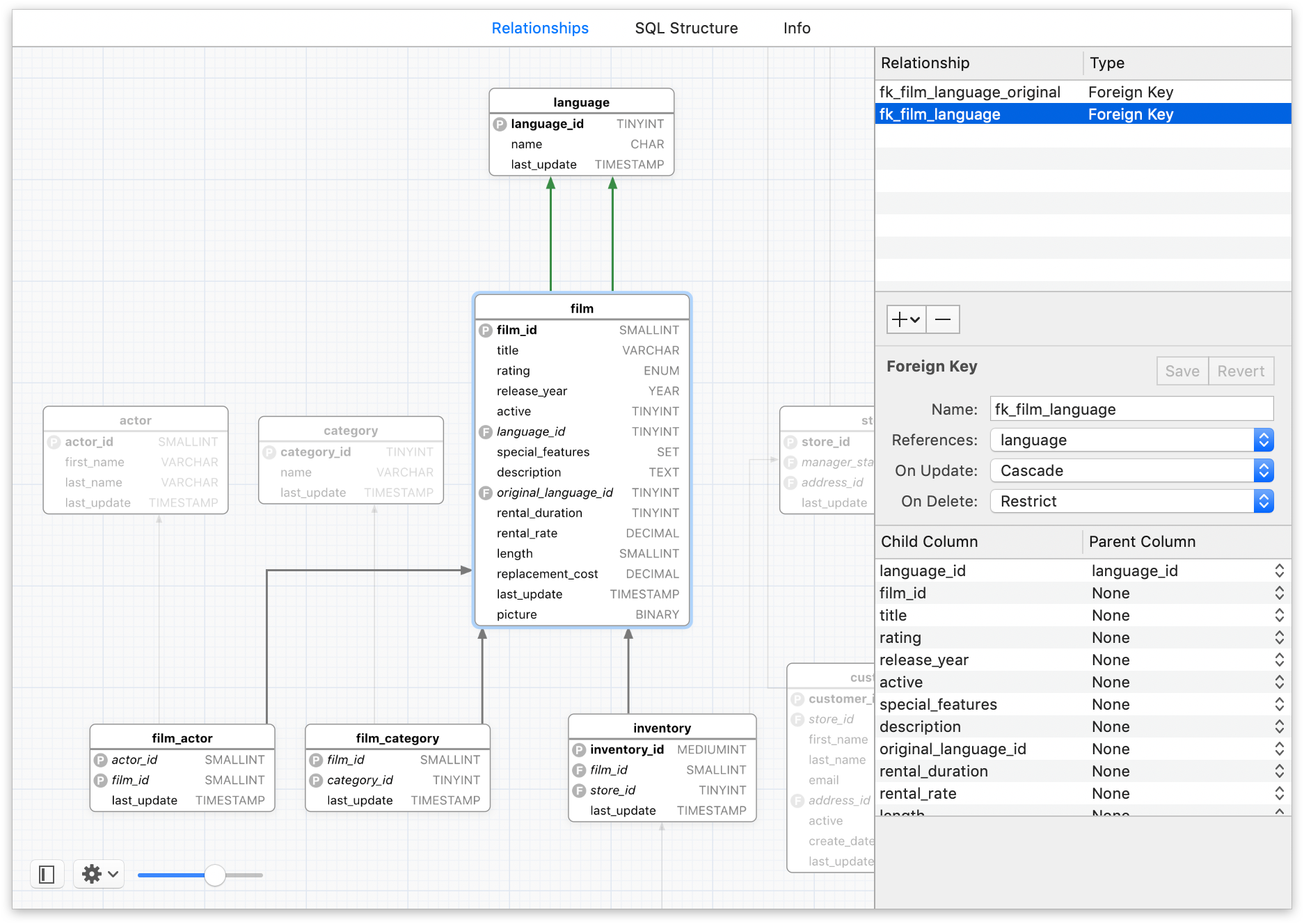
Second, it is widely adopted, so a lot of code is already available. Thanks Aaron.First of all, MySQL is open-source. ibd files does not buy you anything except for spread-out files. If the same display comes up, you did it was kind enough to remind me that spreading. Mysql -uroot select table_schema,table_name from information_schema.tables Next, move the tables into the symlinked databases mysql -uroot -AN -e"SELECT CONCAT('ALTER TABLE ',db,'.',tb,' RENAME ',SUBSTR(db,4),'.',tb,' ') FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema in ('tmpdb1','tmpdb2','tmpdb3')" > /root/MoveTables2.sql Go into mysql and make sure the databases are visible mysql> show databases Ln -s /home/user3/mysql /opt/mysql/data/db3 Ln -s /home/user2/mysql /opt/mysql/data/db2 Go into the OS and create symlinks ln -s /home/user2/mysql /opt/mysql/data/db1 Next, drop the original databases mysql> drop database db1 Next, let's move every table you have db1 to tmpdb1, db2 to tmpdb2, db3 to tmpdb3 mysql -uroot -AN -e"SELECT CONCAT('ALTER TABLE ',db,'.',tb,' RENAME tmp',db,'.',tb,' ') FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema in ('db1','db2','db3')" > /root/MoveTables1.sql Let's start by creating temp databases mysql> create database tmpdb1 If you have three databases (db1, db2, db3), then the folders are:īefore doing anything run this query: mysql> select table_schema,table_name from information_schema.tables Each database woudl reside under that folder. WARNING : The following only works with innodb_file_per_table enabledįor example, suppose your datadir was /opt/mysql/data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
